- Science Chapter 5 Class 10 - Quick Overview on Life Processes
- Download a PDF of the NCERT solutions for class 10 science, chapter 5 on Life Processes
- Topics Covered in Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Life Processes
- Benefits of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Life Processes
- Conclusion
- Life Processes Class 10 Questions and Answers for Exam Preparation
- Links for other Chapter-wise NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
- FAQs
Science Chapter 5 Class 10 – Quick Overview on Life Processes
Do you require help with the Life Processes topic for 10th grade? Nutrition, respiration, transportation, and living beings’ excretion are all discussed in the Science chapter 5 of Class 10—their most important aspects. This chapter will make it easier to grasp the functioning of the human and other animal bodies. In addition to the clear explanations, the students are also provided with well-organised life processes class 10 questions and answers for efficient practice.
ToppersSky NCERT Solutions offers detailed solutions for all exercises in the textbook, important diagrams, and additional questions that are focused on the examination. Every answer is written in plain language and follows the newest syllabus guidelines. Get the NCERT Solutions PDF and get ready for your exams with confidence, thanks to ToppersSky.
Download a PDF of the NCERT solutions for class 10 science, chapter 5 on Life Processes
Topics Covered in Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Life Processes
| List of Topics Covered in Science Chapter 5 | |
|---|---|
| Topics | Subtopics |
| What are Life Processes? | |
| Nutrition | Autotrophic nutrition, Heterotrophic nutrition, Nutrition in human beings |
| Transportation | Transportation in human beings, Transportation in plants |
| Excretion | Excretion in human beings, Excretion in plants |
Benefits of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Life Processes
The NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 – Life Processes, which were created by specialists at ToppersSky, promote the cooperation of pupils in a simple and friendly manner. These solutions present various aids for the students to perform much better during the exams:
- Expert-Curated Content: The answers to the questions in Class 10 Science Chapter 5 have been formed by professional teachers, hence being precise, short and simple. This makes the NCERT Life Processes solutions a trustworthy study material for students.
- Doubt-Solving Support: If ToppersSky students have any doubts at all, they can get the support they need to clear them, as well as to comprehend the life processes concepts better.
- Well-Organised Study Material: The Class 10 Solutions for Life Processes PDF laid down all concepts, definitions and diagrams in a very logical manner, thus providing the students with an effective way of revising.
- Conceptual Learning Through Activities: Students are given a chance to learn the concepts more clearly through performing experiments and relating to nutrition, respiration, transportation, and excretion through real-life examples.
- Easy Download and Revision: As the Class 10 Science Chapter 5 question answers PDF is downloadable, students can carry on their studies and revisions whenever they like, especially before exams.
- Ideal for Quick Revision: The answers are of great help for last-minute review, making sure that students can efficiently remember the main ideas.
- Enhanced Exam Results: Continually working on the Life Processes Class 10 NCERT Solutions will not only improve one’s self-esteem but also result in better marks.
Conclusion
ToppersSky’s NCERT Solutions for Class 10th Science Chapter 5 – Life Processes provide students with clear explanations and well-structured answers for all the topics dealt with in the chapter. These solutions train the students in writing accurate and exam-centred answers. Students are highly encouraged to download and utilize these expert-prepared resources before the exams since it is a good practice. Furthermore, ToppersSky gives access to a lot of study materials and learning resources through its ToppersSky mobile app, which is a great help for effective exam preparation.
Life Processes Class 10 Questions and Answers for Exam Preparation
Q.1 What are the most essential processes for the maintenance of life?
Answer:
Life-supporting processes consist of nutrition, respiration, transportation, excretion, control, and coordination. These functions integral to life, co-ordinate with one another, thus, the organism survives and society functions approvingly. Nutrition, or the intake of food, gives energy and raw materials; respiration metabolizes the food thus releasing energy; transportation via blood flow supplies the body with all the necessary substances; excretion after all these processes eliminates waste materials; while control and coordination help the organism to adjust and respond to changes, whether these changes are from inside or outside the body. If these functions stop, then life support is irretrievably cut off.
Q.2 From where do plants get the necessary materials for photosynthesis?
Answer:
Integration of light, water, carbon dioxide, and chlorophyll without interruption is a must for the plants to execute the light-dependent stage of the photosynthesis process. Stomata are the small apertures located on the plant leaves allowing the gas carbon dioxide to pass into the plant by diffusion. The roots are the parts of the plant that absorb water from the soil and then the water moves through the xylem vessels to the leaves. Sunlight is the most important light source for the plants and it also supplies the energy needed for the process of photosynthesis to occur. The green parts of the plants have chlorophyll pigments that allow them to take up light energy and the green areas of the plant are also the ones that have chloroplasts because of the pigments.
Q.3 What is the mechanism of glucose oxidation in diverse organisms for their energy outputs?
Answer:
The glucose oxidation mechanism in diverse organisms is described as:
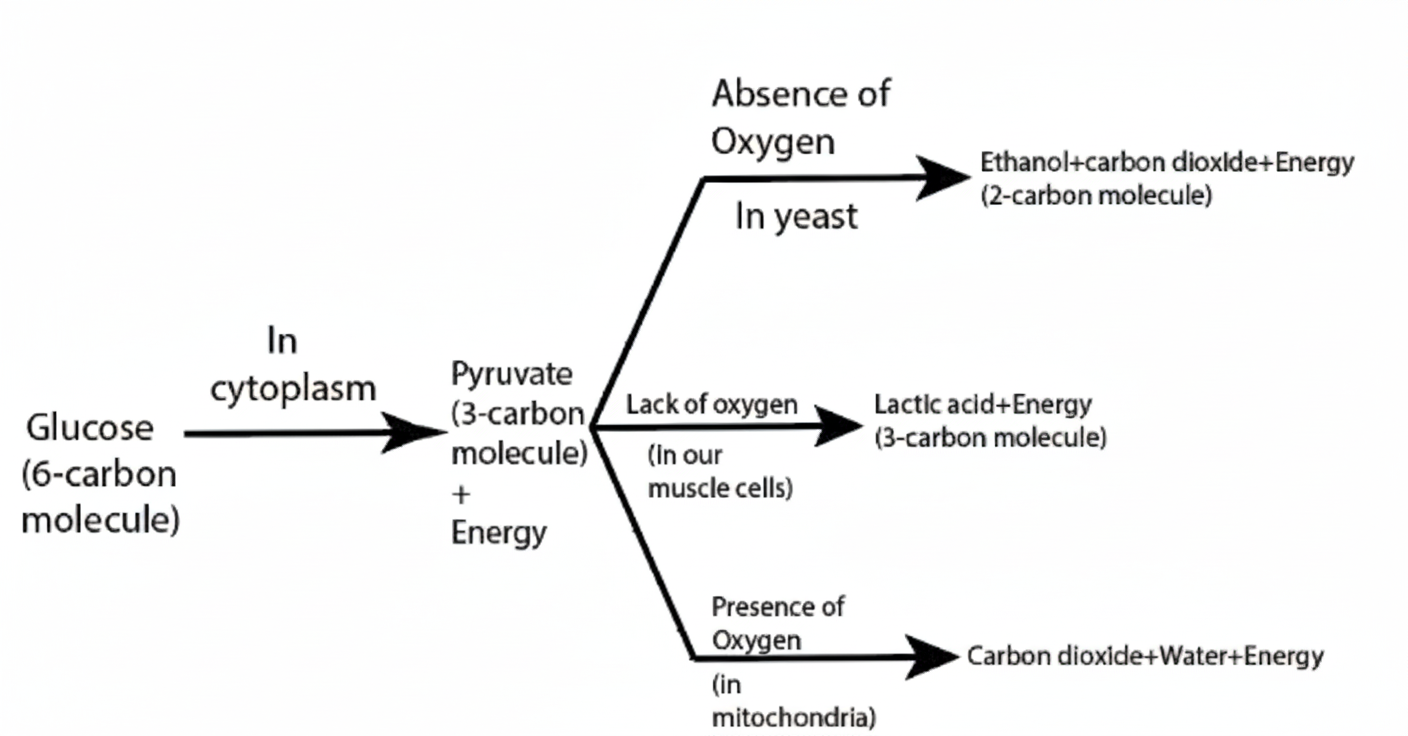
Q.4 Discuss the structure and the function of the nephron in the human body.
Answer:
Nephrons (which are also called filtration units) are the structural and functional units of the kidney. The nephrons number in a large quantity in each kidney. Nephrons are mainly formed by two sections – renal corpuscle and renal tubule.
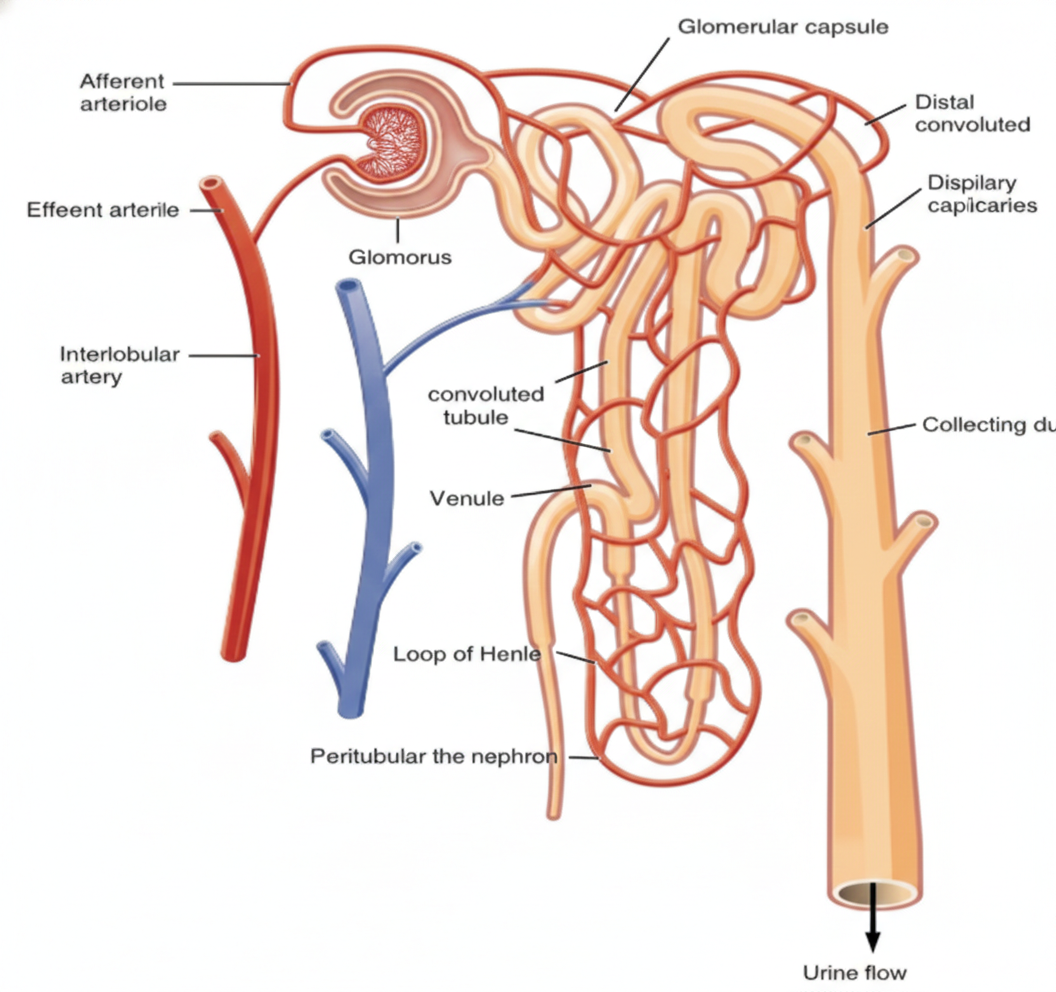
The renal corpuscle consists of a cup-shaped part known as the Bowman’s capsule, along with a group of blood vessels that help in the urine collection, which has already been filtered. The urine composition is altered during its movement through the nephron tubular portion owing to the reabsorption of amino acids, glucose, salts, and water. The reabsorption of water and substances is determined by how much is in the body. The urine then proceeds to the collecting duct of the kidney and is subsequently sent to the ureter, a long tube. Finally, the urine is collected in the urinary bladder.
Q.5 What are the necessary conditions for autotrophic nutrition and what are its by-products?
Answer:
The term “autotrophic nutrition” refers to the biotic process where living beings feed on soil and air materials mainly through photosynthesis. To get this going, certain basic necessities have to be fulfilled, among which are the coming of sunlight as an energy source, carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, water picked up from the soil, and chlorophyll in green plant parts to catch the light energy. In autotrophic nutrition, carbohydrates in the form of glucose are made as food, and oxygen is let out as a by-product, which most living organisms need to survive.
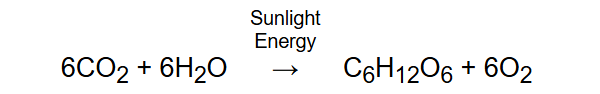
Q.6 What is the function of digestive enzymes?
Answer:
Digestive enzymes play an essential role in the digestive process of food because they metamorphose heavy food substances into light and soluble forms that can be easily absorbed by the body. These enzymes function like biocatalysts, they speed up the chemical reactions and at the same time are not affected. They guarantee that nutrients are converted into usable forms with the help of the rapid digestion process. Every enzyme has its specific nutrient—for instance, amylase acts on carbohydrates, pepsin and trypsin proteins, and lipase does fat. The teamwork of digestive enzymes is one of the most important factors for the body to receive proper nutrition and energy supply.
Q.7 Describe double circulation in human beings. Why is it necessary?
Answer:
Double circulation is a term that refers to the entire human blood circulation process where blood goes through the heart two times for one complete cycle. This kind of circulation ensures the separation of oxygen, rich and oxygen-poor blood in the human body.
The entire process involves two main stages:
1. Pulmonary circulation: In pulmonary circulation, during the process, the right ventricle pumps dirty blood to the lungs. The blood gets reoxygenated and then moves to the left atrium of the heart.
2. Systemic circulation: Oxygen-rich blood is pumped by the left ventricle to the body in systemic circulation. After delivering oxygen and nutrients to the body, the deoxygenated blood returns to the right atrium of the heart.
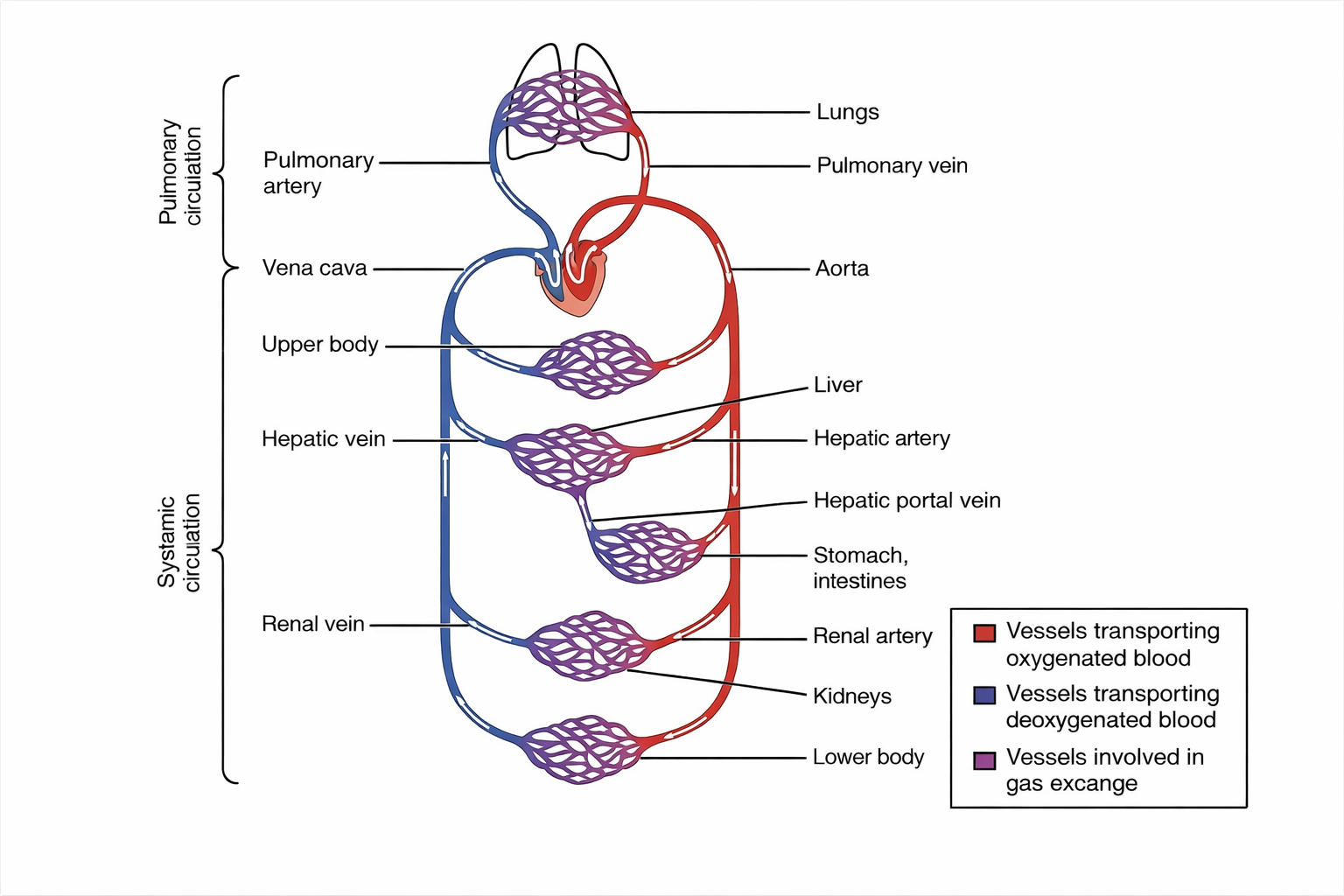
Double circulation is a must because it guarantees the efficient delivery of oxygen to the body cells, keeps high blood pressure, and ensures the entire blood separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated, which is crucial for the proper operation of the human body.
Q.8 What mechanisms are involved in urine amount control?
Answer:
The amount of urine produced is determined by the water and other materials present in the body. Since urine is made up almost solely of water, it is the main factor that is responsible for urine production regulation. When the body has a greater amount of water, then less water will be absorbed back, and more water will be let out from the body and the other way around. There are also some other factors, such as the organism’s habitat, that play a role in the production of the urine, and the main hormone, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), regulating the process has a very significant impact.
Q.9 Describe the process of food transporting in plants?
Answer:
The leaves of plants produce their food by the process of photosynthesis and then the food is moved to the various parts of the plant by the phloem tissues. Phloem is classified as one of the plant tissues using energy in the form of ATP for the movement of food materials. This thereby causes the buildup of osmotic pressure in the tissue that draws in more water to the tissues. The pressure created by osmosis then pushes the material in the phloem to the tissues, which are lower in pressure,e as such supply is not interrupting their demand. The sucrose is one of the food materials that,t when transported into the phloem tissue, needs ATP in the form of energy.
Q.10 What are the differences between autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition?
Answer:
The differences between autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition are:
| Autotrophic Nutrition | Heterotrophic Nutrition | |
|---|---|---|
| Basis of Difference | Definition | Heterotrophic Nutrition |
| Definition | Autotrophic nutrition is a mode of nutrition in which organisms make their own food using simple inorganic substances. |
Heterotrophic nutrition is a mode of nutrition in which organisms depend on other organisms for food. |
| Food Preparation | Organisms prepare their own food by the process of photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. |
Organisms cannot prepare their own food and depend on plants or other animals. |
| Raw Materials Used | Uses carbon dioxide, water, sunlight, and chlorophyll. | Uses complex organic substances as food. |
| Presence of Chlorophyll | Chlorophyll is present (in green plants). | Chlorophyll is absent. |
| Energy Source | Energy is obtained from sunlight. | Energy is obtained from chemical energy stored in food. |
| By-products | Oxygen is released as a by-product. | No oxygen is released as a by-product. |
| Examples | Green plants, algae, some bacteria. | Humans, animals, fungi, non-green plants. |
Links for other Chapter-wise NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
FAQs
1. What are the primary subjects that NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Life Processes deal with?
ToppersSky offers the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Life Processes that cover up all the main topics which have already been a part of the 2025-26 syllabus. Moreover, the list points to four main topics, which are nutrition, respiration, transportation, and excretion in plants and animals. Stepwise solutions are provided for each of the methods so that students can easily understand the biological processes that are the basic support of life.
2. How is the human excretion process which is explained in the NCERT Solutions?
Excretion in humans is a term used to indicate the process of elimination of metabolic wastes from the body. ToppersSky’s NCERT Solutions mention that the kidneys are the main organs responsible for this purification process, which involves blood and the utilisation of very tiny units called nephrons. The solutions describe the phases of filtration, reabsorption, and urine production in a systematic and simple way for easy comprehension.
3. In NCERT Solutions for Life Processes, how do plants transport water and nutrients?
NCERT Solutions on Toppersky reveal that plants use xylem vessels to draw up water and minerals from roots to leaves through transpiration, a process called passive water lift. The phloem, which conducts food in all directions, is used to transport processed food from the leaves to the rest of the plant. These activities are supported and fortified by pictorial representations and logical descriptions, through which they become so simple to remember for examinations.
4. How can NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 be used most efficiently by students for board exam preparation?
- Practising students should:
- Compose stepwise answers compliant with the marking scheme.
- Construct and annotate diagrams as needed.Revise all definitions and differences in tabular form (as per NCERT Solutions).
Not merely memorising answers but rather developing their understanding through additional related questions’ attempts.
5. What will happen if the human body has a shortage of haemoglobin, as stated in Life Processes NCERT Solutions?
The lack of haemoglobin in the blood makes it unable to perform its primary function of oxygen transport, thus leading to the manifestation of signs such as tiredness, lack of energy, and in some cases, anaemia. NCERT Solutions highlight the importance of knowing the consequences and connecting biological functions to everyday health situations, in accordance with the most recent syllabus.






