- Science Chapter 12 Class 10 - Quick Overview on Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
- Download PDF of NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
- Topics Covered in Class 10 Science Chapter 12 - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
- Benefits of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
- Conclusion
- Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Questions and Answers with Solutions
- Other Chapter-wise NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
- FAQs
Science Chapter 12 Class 10 – Quick Overview on Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12, Magnetic Effects of Electric Current, are an important learning resource for students preparing for board exams. This chapter explains the relationship between electricity and magnetism in a clear and structured way. The solutions cover essential topics such as electromagnetism, magnetic fields produced by current-carrying conductors, electromagnetic induction, and the working principles of electric motors and generators. By studying these solutions, students can understand complex concepts easily and improve their answer-writing skills for exams.
The chapter introduces students to the basics of magnetism, including magnetic poles, magnetic field lines, and their properties. It explains how magnetic field lines represent the direction and strength of a magnetic field and discusses the magnetic field patterns around a bar magnet. Students also learn how electric current produces a magnetic field and how the direction of this field depends on the direction of current flow, which is explained using the Right-Hand Thumb Rule.
Further, the chapter describes the magnetic field produced by current flowing through a circular loop. It explains the pattern of magnetic field lines inside and outside the loop and shows how the field strength increases near the centre of the loop. These concepts form the foundation for understanding practical applications such as electromagnets, electric motors, and generators. Overall, NCERT Solutions for Chapter 12 present the topics in a simple, exam-oriented manner, helping students build strong conceptual clarity and perform well in Class 10 board examinations.
Download PDF of NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Add notes section and add an app download function for complete notes
Topics Covered in Class 10 Science Chapter 12 – Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
| S.No. | Topics for Science Class 10 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current |
|---|---|
| 1 | Magnetic Field and Field Lines
|
| 2 | Domestic Electric Circuits |
Benefits of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
- All Class 10 Science Chapter 12 NCERT solutions are in line with the revised Term II syllabus and guidelines, thus making them available for a free demo.
- The solutions of Class 10 magnetic effects of electric current are done by professionals who guide the students in understanding the concepts in a lighter way.
- Magnetic effects of electric current class 10 draws a connection between electricity and magnetic effect or magnetism thereby giving precise answers to the questions.
- In class 10, magnetic effects of electric current solutions, students will come across the concept of magnetic field being a quantity with both magnitude and directional properties which will aid in clearing their doubts.
- Magnetic effects of electric current question answers are provided in chapter-wise PDF format.
- Magnetic effects of electric current NCERT solutions can be accessed easily both through online and offline methods.
- Class 10 science chapter 12 question answers can be extracted from the website.
- Magnetic effects of electric current class 10 NCERT solutions are available to everyone free of cost.
Conclusion
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 provided by ToppersSky guide students through the key concepts of the chapter in a clear and student-friendly manner. Each question is explained briefly and in simple language, helping students gradually build a strong understanding of the subject.
The Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Class 10 questions and answers on ToppersSky include easy explanations, smart techniques, and helpful shortcuts that make it easier for students to remember important laws, rules, and formulas. These methods support effective learning and quick revision. Students can refer to these NCERT solutions after reading the full chapter to clear doubts and strengthen their concepts. This approach improves conceptual clarity, boosts confidence, and helps students prepare better for board examinations.
Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Questions and Answers with Solutions
Q.1 What happens to a compass needle when it is placed with a magnet?
Answer:
Compass needles are little bar magnets, basically. So just like any other bar magnet, when they come close to a bar magnet, the latter’s magnetic field affects the compass needle’s magnetic field by the presence of the magnet. It is the presence of the magnetic fields on both sides that is responsible for the compass needle getting rotated or turned.
Q.2 A round wire loop is lying on a table. Suppose the current in the loop is moving in a clockwise direction, then from the right hand thumb rule, tell me the direction of the magnetic field that passes through the loop and also the one around it?
Answer:
According to the right hand thumb rule, if you see a situation where your right hand’s fingers are curled in the current direction and your thumb is pointing up, then the direction of the magnetic field is the same as that of the thumb.
- Inside the loop: The magnetic field is going downward, i.e., into the table.
- Outside the loop: The magnetic field is going upward, coming out of the table.
So, for a clockwise current, the magnetic field lines
Q.3 What does an earth wire do? What is the reason for earthing metallic appliances?
Answer:
The earth wire plays a role in linking the metal exterior of the electrical equipment to the ground. It is set up in a way that if there happens to be a leak of current, the escaping current will take the path of the earth rather than flowing through the body of a person. This inefficiency in the flow of current through the person and thus avoids electric shocks and makes the system safe. Consequently, metallic appliances being earthed is a must.
Q.4 When does an electric short circuit occur?
Answer:
An electric short circuit occurs under the following conditions:
When the resistance of a circuit becomes very low, causing a sudden increase in current. This may happen when too many appliances are connected to a single socket.
If the insulation of the live and neutral wires gets damaged and they touch each other, function in this case results in the flow of very high current.
Q.5 Two round coils, A and B, are situated near one another. Will there be any current induced in coil B if the current in coil A changes? Support your answer with reasons.
Answer:
Coil B will get induced. When the current in coil A changes, the magnetic field around it also changes, consequently, this changing magnetic field passes through coil B and brings about the production of electric current in coil B. The phenomenon is known as electromagnetic induction.
Q.6 An electron beam travels from the back of the wall to the front and, at the same time, is directed to the right. What do we infer regarding the magnetic field’s polarity in that situation?
Answer:
Electrons are moving in a direction opposite to that of the current, hence, the current is flowing from the back wall to the front. By using Fleming’s left hand rule, if the thumb (force) points to the right, then the first finger (magnetic field) down and the second finger (current) from the back wall to the front.
Q.7 List three sources of magnetic fields.
Answer:
Three common sources of magnetic fields are:
- Current-carrying conductors
- Permanent magnets
- Electromagnets
Q.8 Draw magnetic field lines around a bar magnet.
Answer:
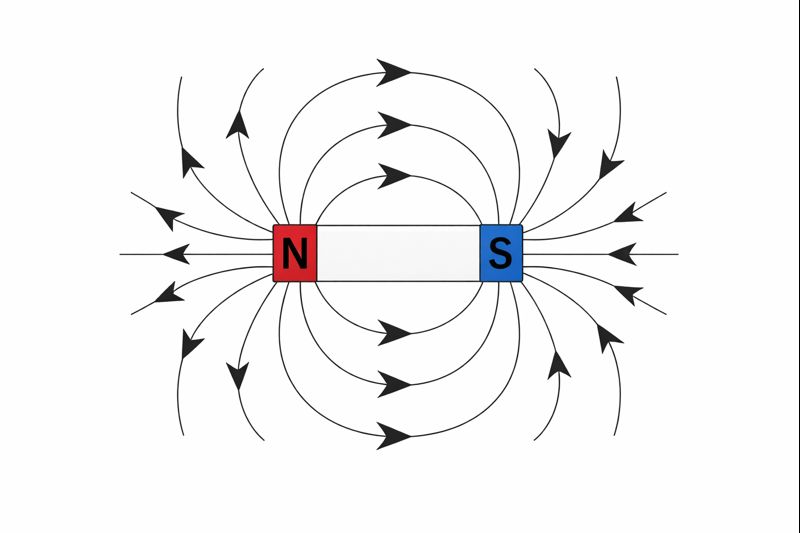
The lines of the magnetic field of a bar magnet lead to the south pole and come from the north pole outside the magnet. While moving in the magnet itself, the field lines are directed from the south pole to the north pole and hence are forming closed and continuous loops. The poles have these lines of force closer together which means that the magnetism is very strong at the poles, as is indicated in the drawing.
Q.9 What is the reason behind a solenoid acting as a magnet? Is it possible to find out the north and south poles of a solenoid carrying current by using a bar magnet? Justify your explanation.
Answer:
A solenoid is basically a cylindrical coil consisting of numerous loops of insulated copper wire. The moment electric current passes through the solenoid, it generates a magnetic field by the formation of a number of circular magnetic lines around it. The current’s magnetic field of the solenoid is very much similar to that of a bar magnet in all aspects. One of the solenoid’s ends acts as a north pole and the other one as a south pole.
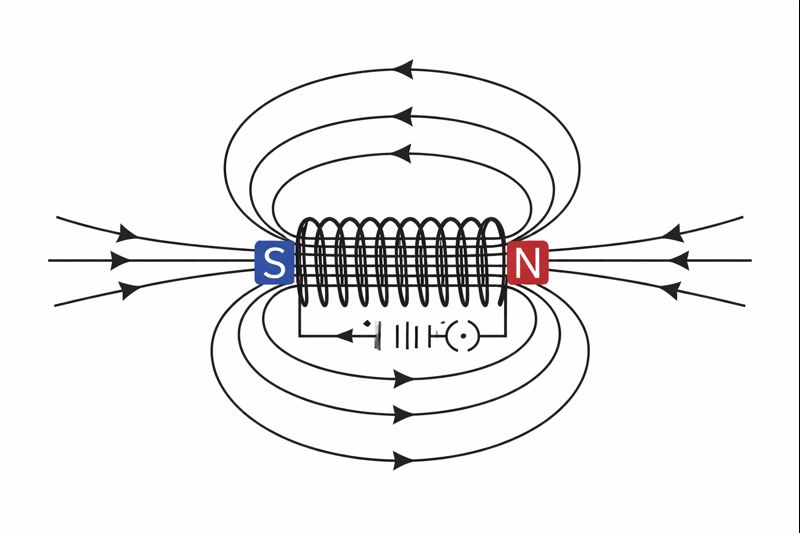
Moreover, the poles of a solenoid can be located through the use of a magnet. If the north pole of a magnet is brought very close to the solenoid end that is wired to the battery’s negative terminal, the bar magnet will be pushed away. Now, if we remember the fact that like poles do repel each other, it indicates that the end which is wired to the negative terminal behaves as the north pole of the solenoid. Thus, the end that is connected to the positive terminal acts as the south pole of the solenoid.
Q.10 Draw a labelled diagram of an electric motor. Explain its principle and working. What is the function of a split ring in an electric motor?
Answer:
An electric motor operates as a machine that transforms electrical power into mechanical power. The system operates according to the magnetic effect of electric current, which states that a conductor carrying current will experience a force when it enters a magnetic field. The force causes the conductor to initiate its movement.
Principle of an Electric Motor
The implementation of electric current through a rectangular coil creates forces which operate on its two opposing sides with opposing direction. The resultant force causes the coil to develop a continuous rotational motion.
Working of an Electric Motor
The switch closure enables current to pass through the coil system which includes all ABCD segments. The current flows from A to B in arm AB and from C to D in arm CD. The magnetic field exerts its force from the left side to the right side. According to Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule, a downward force acts on arm AB and an upward force acts on arm CD. The coil begins to rotate in an anticlockwise direction because of the two forces which move in opposite directions.
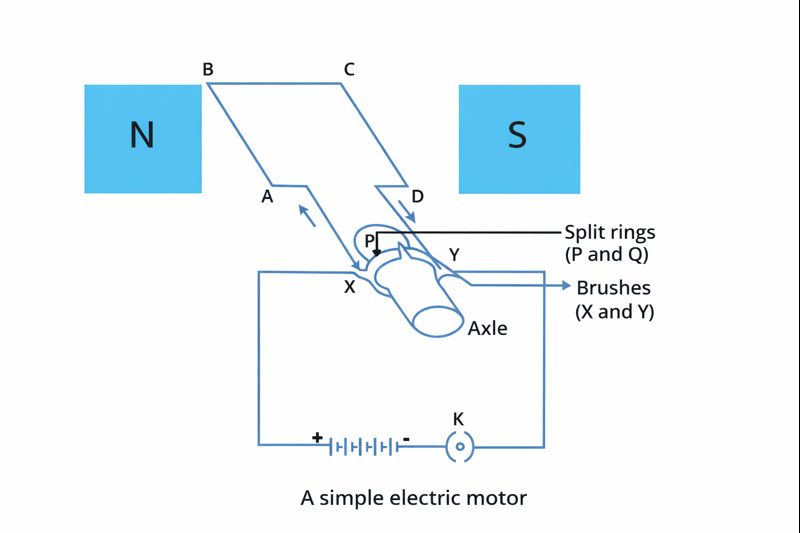
The split rings after completing their half rotation change their point of contact with the carbon brushes. The current flow in the coil changes direction because of this. Current now flows through the system in the DCBA direction. The current reversal happens after every half rotation but the coil maintains its constant rotation direction. The coil maintains its rotational movement towards one specific direction.
Function of Split Ring (Commutator)
The split ring functions as a commutator which enables the coil to switch its current direction after every half rotation. This process enables the coil to maintain its rotational movement while preventing any periods of inactivity.
Other Chapter-wise NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
FAQs
1. What is the magnetic effect of electric current?
When electric current flows through a conductor, it produces a magnetic field around it. This phenomenon is called the magnetic effect of electric current. It forms the working principle for devices like electric motors, generators, and electromagnets.
2. Where can I find Class 10 Science Chapter 12 question answers?
Vedantu provides expert-verified NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12. These solutions cover all in-text and exercise questions, helping students understand concepts accurately and prepare for exams. The answers align with the latest CBSE guidelines.
3. What is Fleming’s left-hand rule used for?
Fleming’s left-hand rule is used to determine the direction of force experienced by a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field. It is crucial for understanding the working of an electric motor. The thumb indicates force, the forefinger indicates field, and the middle finger indicates current.
4. What is electromagnetic induction?
Electromagnetic induction is the process of generating an electric current in a conductor by changing the magnetic field around it. This principle, discovered by Michael Faraday, is the basis for the functioning of electric generators and transformers.
5. What is the function of an electric motor?
An electric motor is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. It works on the principle that a current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field experiences a force, which causes rotation. Motors are used in fans, washing machines, and refrigerators.







