- Science Chapter 6 Class 10 - Quick Overview on Control And Coordination
- Download a PDF of the NCERT Solutions for class 10 Science, Chapter 6 on Life Processes
- Ch 6 Science Class 10 Quick Overview of Detailed Structure of Topics Covered
- NCERT Science Chapter 6 Control and Coordination Class 10 – Important Points
- Advantages of Utilizing ToppersSky Class 10 Control and Coordination NCERT Solutions
- Conclusion
- Control And Coordination Class 10 Questions And Answers For Better Exam Preparation
- Links for Chapter-wise NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
- FAQs
Science Chapter 6 Class 10 – Quick Overview on Control And Coordination
Class 10th Science Ch-6 Control and Coordination introduces students to the various ways in which living beings react to environmental changes. Among the topics dealt with in this chapter, the nervous system, hormones, and movements of plants are the most important ones. The Control and Coordination Class 10 NCERT Solutions bring these concepts to the level of students, thus making learning and remembering less difficult.
ToppersSky gives structured and simple-to-comprehend solutions for each and every question in this chapter. In addition, students can take a look at NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science on ToppersSky to get familiar with other important chapters and have a detailed study of them. Each answer is written in such a manner that the common man can understand the concept. These solutions are going to be really helpful for exam preparation, since every process is explained clearly and in an orderly manner. The students are allowed to download the NCERT Solutions PDF and start their preparation with full confidence.
Download a PDF of the NCERT Solutions for class 10 Science, Chapter 6 on Life Processes
Add notes section and add an app download function for complete notes
Ch 6 Science Class 10 Quick Overview of Detailed Structure of Topics Covered
| Topics | Subtopics |
|---|---|
| Animals – Nervous System |
|
| Coordination In Plants |
|
| Hormones In Animals |
|
NCERT Science Chapter 6 Control and Coordination Class 10 – Important Points
Nervous System
The nervous system is composed of a series of organs and cells that send electrical signals to one another in order to regulate and synchronize the different body functions.
- Central Nervous System (CNS): This brain and spinal cord-based system is primarily responsible for all information processing and the issuing of commands.
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): The PNS includes all the nerves that provide the physical connection between the CNS and different body regions.
- Neurons: Neurons are the basic building blocks, and they are the smallest components of the nervous system. Their main responsibility is to carry impulses.
- Reflex Action: It is a quick and involuntary response to an external stimulus which is intended to protect the body.
Brain Structure and Functions
- Cerebrum: The brain’s portion which defines human activities by free will, reasoning, remembering, intelligence, and sensing, is called cerebrum.
- Cerebellum: The area of the brain known as cerebellum assists in balancing the body and coordinating the actions of the muscles.
- Medulla Oblongata: Involuntary functions like breathing, heart beating, and maintaining blood pressure are under the control of this part of the brain.
Endocrine System
In the case of the endocrine system, it is hormones that take control of the entire process of the growth and metabolism and coordination.
- Hormones: They are the chemical messengers that get released straight into the bloodstream.
- Pituitary Gland: The reason for the pituitary gland being called the “master” is due to the fact that it has the power to control all the glands in the endocrine system.
- Thyroid Gland: The organ which is directly responsible for the secretion of the thyroid hormone thyroxine and the control of metabolism is the thyroid gland itself.
- Pancreas: Consequently, the pancreas plays a major role among its many functions, it is hence the one that is hence the one that produces insulin, the hormone which regulates blood sugar within the normal range.
- Adrenal Glands: The adrenal glands are chiefly responsible for producing adrenaline, a hormone that enables the body to rapidly get its act together and handle stress and emergencies.
Coordination in Plants
Plants are sensitive to environmental changes and they react with the help of hormones instead of nerves.
- Tropism: It is the growth response of the plants towards or away from a stimulus, for instance, phototropism and geotropism.
- Nastic Movements: The non-directional reactions of stimuli are like the Mimosa leaves folding upon touch.
- Plant Hormones: These include auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, abscisic acid, and ethylene which are in charge of the growth and movement regulation.
Advantages of Utilizing ToppersSky Class 10 Control and Coordination NCERT Solutions
- The NCERT solutions by ToppersSky for class 10 science chapter 6 control and coordination give the reader a thorough and very clear understanding of the concepts like the nervous system, hormones, reflex actions, and plant coordination.
- Control and Coordination class 10 NCERT solutions give clear and easy to follow answers that make complicated biological processes to be easily understood and remembered.
- Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Question Answers come with well-drawn diagrams and illustrations that are very useful for students in getting a clear understanding of neurons, synapses, and glands.
- These solutions are strictly in accordance with the syllabus and thus provide complete coverage and exam-oriented preparation.
- ToppersSky also offers other learning materials like brief notes, major concepts, and model questions to support students in their quest for being very clear in concepts.
Conclusion
ToppersSky’s Class 10 Control and Coordination NCERT Solutions are a helping hand for students when it comes to the understanding of this serious chapter. The nervous system, hormones, reflex actions, and plant responses are some of the key areas that control and coordinate the functioning of the body. Thanks to the clear explanations and the orderly answers students can master these topics. Since previous years’ question papers usually have 5–7 questions from this chapter, thorough preparation is a must. ToppersSky’s expert-curated solutions are the best way for students to raise their comprehension, confidence, and performance in exams to the highest possible level.
Control And Coordination Class 10 Questions And Answers For Better Exam Preparation
Q.1 What control and coordination are processes in living organisms?
Answer:
Control and coordination are the most important processes that allow organisms to perform their various functions and react to the environment. In the human case, the nerves and hormones take the responsibility of that.
Q.2 How Does Phototropism Happen in Plants?
Answer:
Phototropism is described as the orientation of a plant part towards or away from a light source. Among plant parts, shoots exhibit positive phototropism while roots exhibit negative phototropism. The main reason is the slow spreading of the plant’s hormone auxin, especially IAA (indoleacetic acid), which is the main actor in the phototropic movement of plants. When one side of the plant receives light, IAA molecules move to the other side (shaded) of the stem. The side that is exposed to light will not have the production of IAA, but the dark side will go through cell division and elongation. As a result, the two sides of the stem will be having a different growth rate, with the dark side being the fastest of all. That is why the shot turns to the light.
Q.3 Draw the Structure of a Neuron and Explain Its Function.
Answer:
The neuron is the basic unit both structurally and functionally of the nerve system. A neuron consists of three major parts: the axon, dendrite and the cell body.
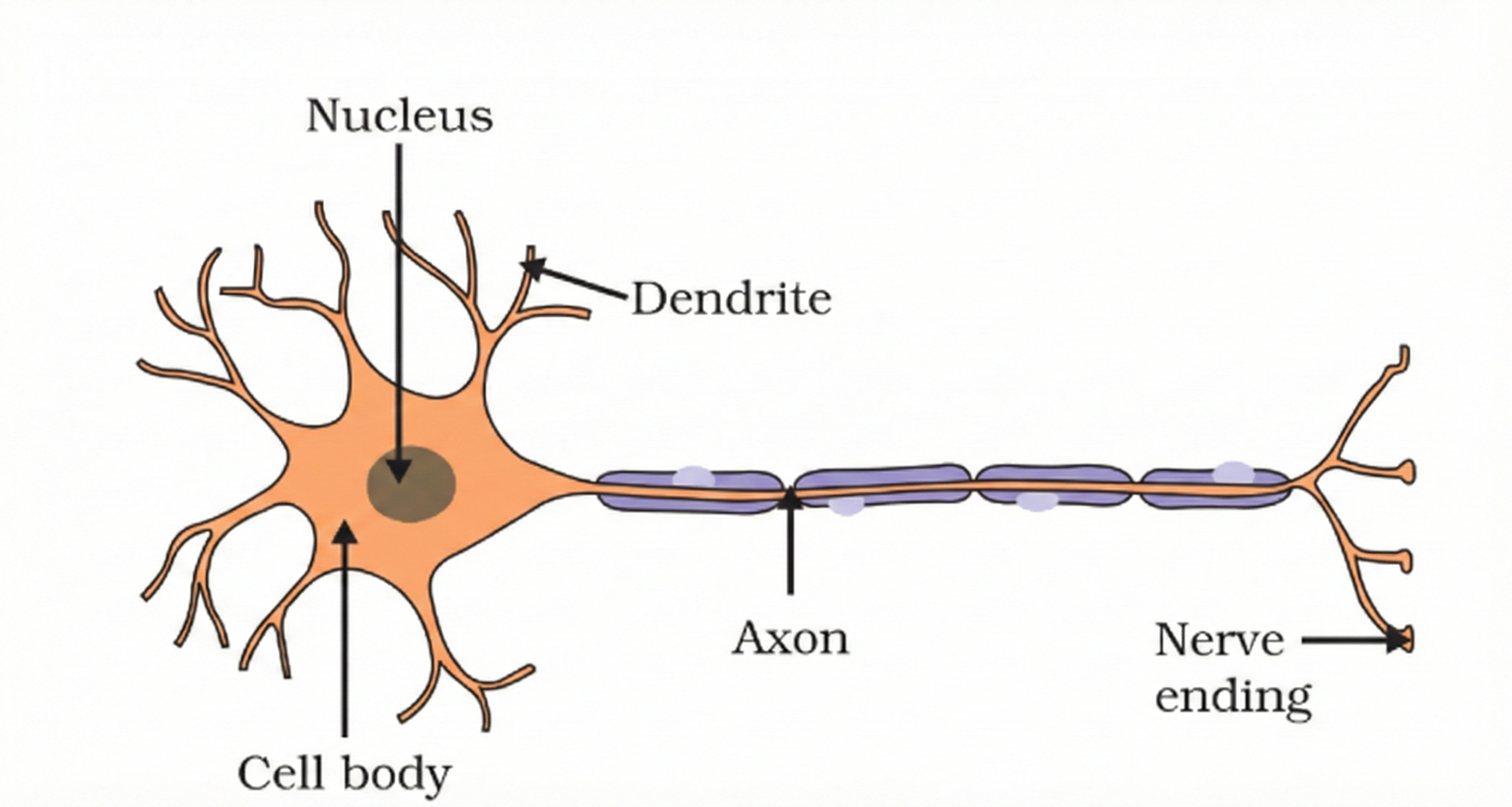
A neuron does many things, one of which is to:
- Transmit impulses from the outer environment to the brain or spinal cord.
- Coordinate the brain/spinal cord with other organs.
Q.4 How does chemical coordination happen in plants?
Answer:
Plants react to stimuli in such a way that they show movement by their leaves, thereby losing or gaining movement in that part of the plant. The entire growth process in which the plant eventually reacts to the environment is regulated by special types of chemical compounds called plant hormones or phytohormones. Plant hormones are usually produced in certain areas of a plant and are then transported to other regions of the plant. Where there is a requirement of hormone generated in the roots, it is then carried to the rest of the plant. There is a lengthy catalog of plant hormones but auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, abscisic acid, and ethylene are the principal ones. Among these, auxins, gibberellins, and cytokinins are grouped with ethylene as growth promoters while abscisic acid is classified as a growth retardant.
Q. 5 What Role does the Brain play in a Reflex Action?
Answer:
Pinchinesis is a quick, involuntary response (of the overall system of both mental and physical variables) as opposed to man’s sharply reactive responses to immediate environmental stimuli. The sensory nerves that signal the stimuli are connected to the motor nerves, which cause the muscle movement to take place. A reflex arc is a connection between perceiving the signal from the receptors (input) and effecting an immediate response to it (output) through the effectors. The reflex arc functions as a communication channel between the receptors and the effectors in a reflex action.
The signal is transmitted by the sensory and motor neurons that have connections in the spinal cord. Even though the reflex arcs begin in the spinal cord, the information (input) is transmitted to the brain. The only thing that the brain is aware of is the signal and the response that has taken place. This knowledge is kept in the brain’s memory. This is what helps in the conditioning of certain reflexes. The brain, however, does not play any role in the production of the response.
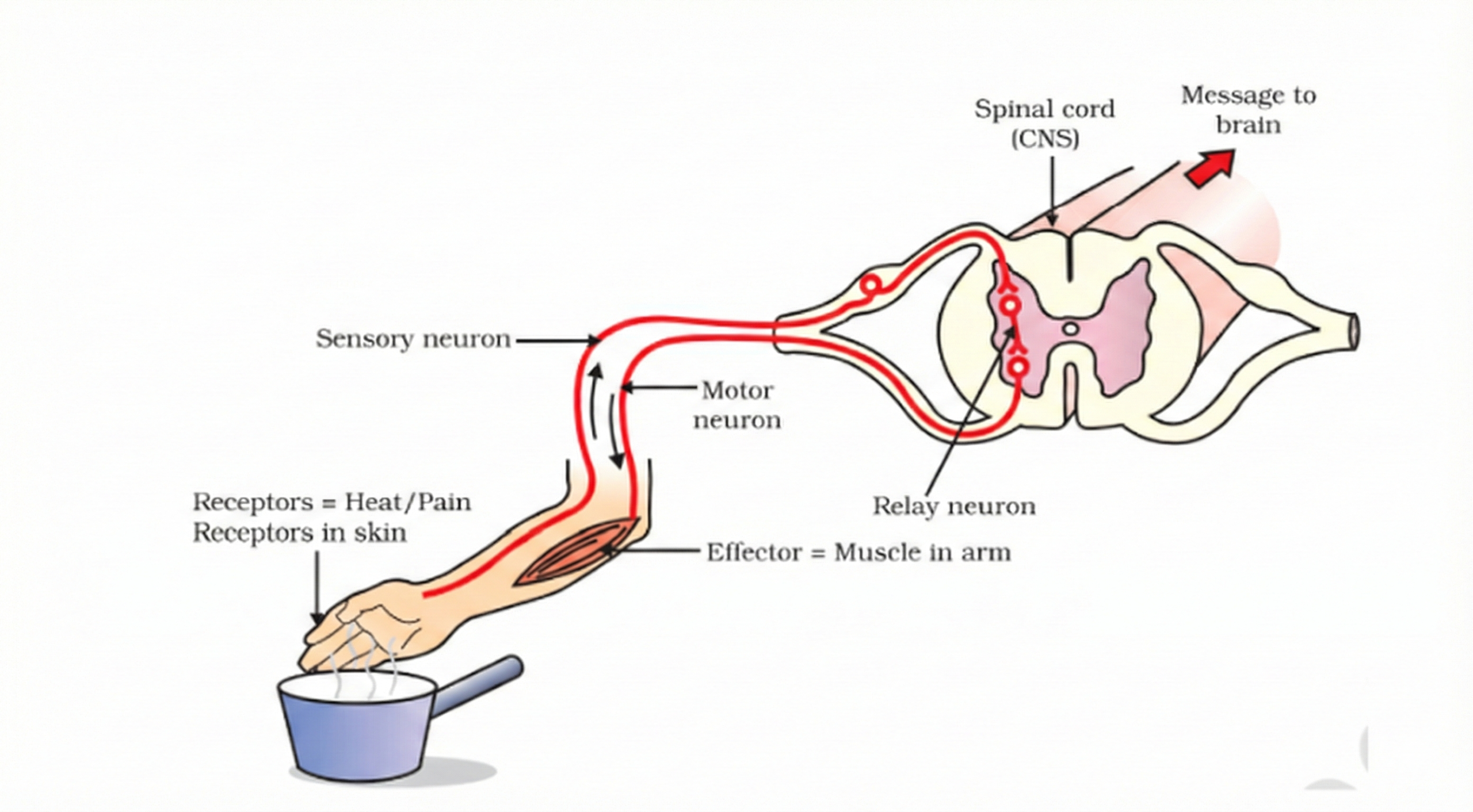
Q.6 Which Signals Will Get Disrupted in Case of a Spinal Cord Injury?
Answer:
If there is a spinal cord injury, then nerve signalling of all kinds will be influenced. This will affect the flow of signals from the receptors to the brain and the brain’s response to the effectors, especially the motor neurons.
Q.7 What is the Need for a System of Control and Coordination in an Organism?
Answer:
Coordination is the process of maintaining body functioning in response to changes in the body by working together for distinct integrated body systems. All of the motions that occur as a result of stimuli must be meticulously coordinated and controlled. Controlling how you react to stimuli aids in the development of more efficient response mechanisms. When all of the stimuli and their effects are taken into account, the organism’s ability to function efficiently is dependent on the coordination of numerous reactions. As a result, multiple physiological processes and responses must be synchronised. The neurological and muscular systems in animals offer movement control and coordination. Phytohormones are responsible for controlling and coordinating plant behaviour.
Q.8 How are Involuntary Actions and Reflex Actions Different From Each Other?
Answer:
Involuntary actions are beyond our ability to control. We can’t control the movement of food in the alimentary canal, for example. These actions, on the other hand, are directly controlled by the brain. On the contrary, reflex actions like withdrawing the hand upon touching a hot surface are very quick and do not need any mental processing. Hence, it is suggested that, compared to involuntary functions, reflex activities are not mediated by the brain. It is impossible to condition biological activities such as heartbeat and peristalsis; however, reflex actions might be chastened. One can draw the inference that all involuntary acts are reflex actions to some extent, but not conversely.
Q.9 Compare and Contrast Nervous and Hormonal Mechanisms for Control and Coordination in Animals.
Answer:
The difference between nervous and hormonal mechanisms is as follows:
Compare and Contrast Nervous and Hormonal Mechanisms for Control and Coordination in Animals
| Basis of Comparison | Nervous Mechanism | Hormonal Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Nature of signal | Electrical impulses | Chemical messengers (hormones) |
| Speed of response | Very fast | Slow |
| Mode of transmission | Through nerve fibers | Through blood |
| Duration of effect | Short-lived | Long-lasting |
| Area of effect | Specific and localized | Widespread |
| Organs involved | Brain, spinal cord, and nerves | Endocrine glands |
| Example | Reflex action | Action of insulin, adrenaline |
In animals, nervous and hormonal mechanisms are both involved in managing and directly coordinating their activities. The nervous system reacts almost immediately to the stimuli, whereas the hormonal system takes care of the long-lasting processes, like the ones mentioned: growth, metabolism, and development.
Q.10 Which hormone is classified as a plant hormone?
Answer:
Cytokinin is a plant hormone. It is formed in the developing parts of the plant like root, fruit, and seed. Cytokinins have a major part of the plant’s life cycle as they are responsible for cell division, elongation, and tissue rejuvenation in plants. While hormones like insulin, thyroxin, and estrogen perform their functions in both animals and humans, cytokinins are exclusively involved in the plant’s physiological processes.
Links for Chapter-wise NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
FAQs
1. What are the chief ideas highlighted in the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Control and Coordination?
The NCERT Solutions of Class 10 Science Chapter 6 include many different concepts such as the nervous system, reflex actions, the coordination in the plants, the presence of hormones in animals, movements that can be controlled and those that can’t, and the structure of the brain along with the functions of chemical coordination (hormonal). A step-wise approach is adopted in providing solutions that not only make the concepts easy to understand but also ensure clarity of the concepts to the students.
2. What is the role of the human brain in control and coordination according to NCERT Solutions?
The human brain is the principal control of the body which holds all the functions under its command and it does so by both controlling and regulating. Besides these, it also controls learning, memory, emotions, automatic ones like breathing, and even the processes of sensory input, processing, and output. The solutions provide a very clear and detailed explanation of the respective roles of the cerebrum, cerebellum, and medulla oblongata with their functional distinctions.
3. NCERT Solutions point out similarities and differences between phototropism and geotropism in plants in what manner?
NCERT Solutions state that phototropism is a light-induced movement in plants during which the upper part of the plant leans toward the light and geotropism is a movement caused by gravity in which the roots grow downwards. Botanical motions are chronicled stepwise and illustrated with diagrams to make it easier to comprehend the process.
4. In what way does the NCERT Solutions technique support learners in their exam preparation?
The method is straightforward and structured, with great detailing on to-the-point solutions and proper scientific terminology. The solutions consist of application-based questions, higher-order thinking questions, and beautifully sketched diagrams that all help the learners to prepare for the exams in a good manner.
5. What are the common diagram-based questions about Control and Coordination?
The most common diagram-based questions from this chapter are:
Neurons labeled with their respective components indicating the axon, dendrite, cell body, and synapse are shown in the picture.
The illustration shows the reflex arc which includes and consists of the receptor, the sensory neuron, the spinal cord, the motor neuron, and the effector.
Panels of the brain showing the major areas of the cerebrum, cerebellum, and medulla are also among the questions.







