- Science Chapter 7 Class 10 - Quick Overview on How Do Organisms Reproduce
- Quick Insights of How Do Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Solutions
- Download a PDF of the NCERT solutions for class 10 science, chapter 7 on How Do Organisms Reproduce
- Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 7 How Do Organisms Reproduce: Quick Overview of Topics
- Class 10 NCERT Solutions Chapter 7 – Important Topics From How Do Organisms Reproduce
- Benefits of NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 7 – How Do Organisms Reproduce
- Conclusion
- Master How Do Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Questions and Answers With Our Expert Solutions
- Links For Chapter-wise NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
- FAQs
Science Chapter 7 Class 10 – Quick Overview on How Do Organisms Reproduce
How Do Organisms Reproduce Class 10 NCERT Solutions contemplation of a very significant topic in biology—the way living organisms create new individuals and transmit genetic characters to the next generation. By this lesson, students are able to pinpoint the exact location where genetic material is passed on to the next generation from the parents through the genes. It also gives birth to the notion of slow and gradual changes in the living beings throughout the ages, thus making it easier for students to realize the concept of life being continuous and diverse at the same time. The questions and answers of this chapter do reproduce in a systematic way, thereby simplifying the whole process of grasping the biological importance of the development of life and evolution.
Quick Insights of How Do Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Solutions
Class 10 Science Chapter 7 opens the discussion on reproduction in a lucid manner and presents the different ways by which organisms secure the existence of their kind. The chapter discusses the asexual and sexual modes of reproduction thoroughly.
The questions and answers of this chapter present very brief but to the point descriptions of the reproduction systems in the various types of organisms, as well as the methods of fertilization and development.
How Do Organisms Reproduce Class 10 solutions also stress on the subject of human reproductive health and the necessity of being informed about the different reproductive processes.
These solutions help the students gauge their comprehension of the central ideas and through the structured explanations, bring about the development of conceptual clarity.
The entire syllabus covered in How Do Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Solutions is in accordance with the modified academic syllabus for the ongoing session.
Download a PDF of the NCERT solutions for class 10 science, chapter 7 on How Do Organisms Reproduce
Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 7 How Do Organisms Reproduce: Quick Overview of Topics
| Topic | Subtopics Covered |
|---|---|
| Introduction to Reproduction |
|
| Asexual Reproduction |
|
| Sexual Reproduction in Plants |
|
| Sexual Reproduction in Humans |
|
| Reproductive Health |
|
Class 10 NCERT Solutions Chapter 7 – Important Topics From How Do Organisms Reproduce
The students will be able to understand the important aspects of Chapter 7 easily and in an organized manner by means of the Class 10 NCERT Solutions. The topics that are considered important from How Do Organisms Reproduce are elaborated upon well which enables good exam preparation.
Modes of Reproduction
Every living thing generates new individuals through a method that is either asexual or sexual. Only one parent is needed in asexual reproduction and the offspring are genetically identical to the parent. In sexual reproduction, male and female gametes fuse together first and then new offspring inherit different genetic traits from their parents.
Reproductive Structures and Processes
Different animals and plants have various kinds of reproductive structures. For example reproductive organs in animals and flowers in plants are the ones that produce and transfer the gametes. Besides the gamete formation, pollination, fertilisation and embryo development are the processes that contribute to successful reproduction.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Reproductive Modes
On one hand, asexual reproduction allows for fast growth of the population while on the other it does not provide genetic variation which makes the species more susceptible to the changes in the environment. Sexual reproduction, though it consumes a lot of time and energy, is the only way through which genetic diversity and consequently, adaptability and survival is the species’ best quality.
Reproductive Health and Related Issues
Reproductive health is a wide area of concern that covers puberty, menstruation, fertility, contraception, sexually transmitted infections, and infertility. The knowledge of these topics is important so that one can keep the overall health and well-being maintained.
Benefits of NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 7 – How Do Organisms Reproduce
- The ToppersSky Class 10 NCERT Solutions for Science Chapter 7 – How Do Organisms Reproduce are multiple, aiding the students to have a complete understanding of the chapter and be able to do very well in the examinations too.
- The solutions present thorough elucidations along with those for the whole chapter, and to guide the students through the learning process, taking it in an easy and systematic way.
- Each solution has been unerringly prepared with a view to utmost accuracy and clarity, and thus, the students are getting the concepts without any mix-up.
- The focal points of the chapter, such as the reproduction methods, have been robustly elucidated through clear elucidation of asexual and sexual reproduction modes.
- The clarity and conciseness of the explanation,disregarding other things, have been accompanied by the need for proper scientific terms which were commensurate with the Class X standard.
- The concepts associated with reproductive health, like puberty, menstruation, fertility, contraception, sexually transmitted infections, and infertility, have been properly contextualised and made significant through the discussions.
- The solutions of Chapter 7 not only practice but also present question types alternately, thus boosting students’ analytical and problem-solving skills.
- Explanations in a step-by-step manner are the pathways for students to grasp the processes and graphs well, which is the very core requirement to produce well-structured answers in examinations.
Conclusion
ToppersSky’s NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 – How Do Organisms Reproduce, are definitely a beneficial learning aid for the Class 10 students. The solutions make the biological concepts easy to understand and are thus very helpful in students’ learning the hard topics. The elaborated explanations are a great help in forming the right concepts, and they also enhance the overall comprehension of the NCERT-based concepts. Through ToppersSky’s chapter-wise solutions, the pupils will get the necessary support to develop their confidence in this major chapter and hence prepare well. Diagramming and writing structured answers regularly, especially, is essential in the successful mastering of Class 10 Science Chapter 7.
Master How Do Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Questions and Answers With Our Expert Solutions
Q.1 What is the main function of DNA replication in reproduction at the biological level?
Answer:
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) is the genetic material that makes up the living part of a cell and the cell’s nucleus where it is found in the form of chromosomes. It specifies wholly, together with the rest of the genes, the organism’s physical and biological attributes. The reproductive process entails DNA replication, hence it becomes possible for the transfer of genetic material from parents to their offspring.
A child obtains two DNA strands – one from the mother and the other from the father, which is the primary reason that children resemble their parents. Careful DNA replication guarantees that some characteristics will be inherited from one generation to the next. Besides, in sexually reproducing organisms, DNA replication brings about minute differences, which are then considered to be the advantages of survival and help the species to adapt to new environments. Thus, DNA replication is the process that continues to keep evolution and the gradual process of inheritance alive.
Q.2 Why is variation viewed as an advantage for a species but not necessarily for an individual organism?
Answer:
The presence of variation in a species is a great advantage because it opens the door for the species to penetrate different places in the environment. A good example is that the extreme water temperature rise may result in the death of almost all bacteria, but a few of them that have the resistant trait may carry on as the heat-friendly ones. These surviving mutants will be the new generation of the species. Variations would mean that the population would be wiped out. On the other hand, the individual may not always benefit from the variations, as some variations may be against the weak or the strong being. Thus, it can be said that while difference is a factor that assures the survival of a species, it doesn’t mean every individual will.
Q.3 What is the main function of the seminal vesicles and the prostate gland?
Answer:
The seminal vesicles and the prostate gland are mainly responsible for the feeding and transportation of sperms. They are the main suppliers of the fluids that eventually get mixed with the sperms to create the semen. The secretions furnish a liquid medium that facilitates the movement of sperms in the reproductive tract. They also cover the sperms and secure them during the process of transport. Semen is a mix that carries substances such as fructose, calcium, and enzymes, which serve as energy sources and are also responsible for the life of sperms for a period of up to several days, until fertilization occurs.
Q.4 What are the benefits of sexual reproduction compared to asexual reproduction?
Answer:
Out of all the benefits of sexual reproduction compared to asexual reproduction, one major factor is the increased genetic diversity. This is because the young ones get characteristics from both mother and father. These variations, in fact, increase the likelihood of a species surviving in other conditions that may not be favourable, and thus, the variations created through sexual reproduction are more stable and adaptable than those created through asexual reproduction, where the genetic material is almost perfectly copied, and the same traits are transmitted. Sexual reproduction, while inefficient in terms of the number of offspring produced, has the advantage that the resulting variations are more viable and thus evolution and long-term survival of species will also depend on them.
Q.5 How does binary fission differ from multiple fission?
Answer:
Binary fission and multiple fission are both means of asexual reproduction but they are dissimilar in terms of the process of new individual formation. In binary fission, one parent organism splits into two identical daughter cells after the nucleus undergoes one division. This biological mechanism is generally carried out in favorable conditions and is characteristically observed in the case of Amoeba and bacteria. The division is simple and rapid, resulting in two separate individuals.
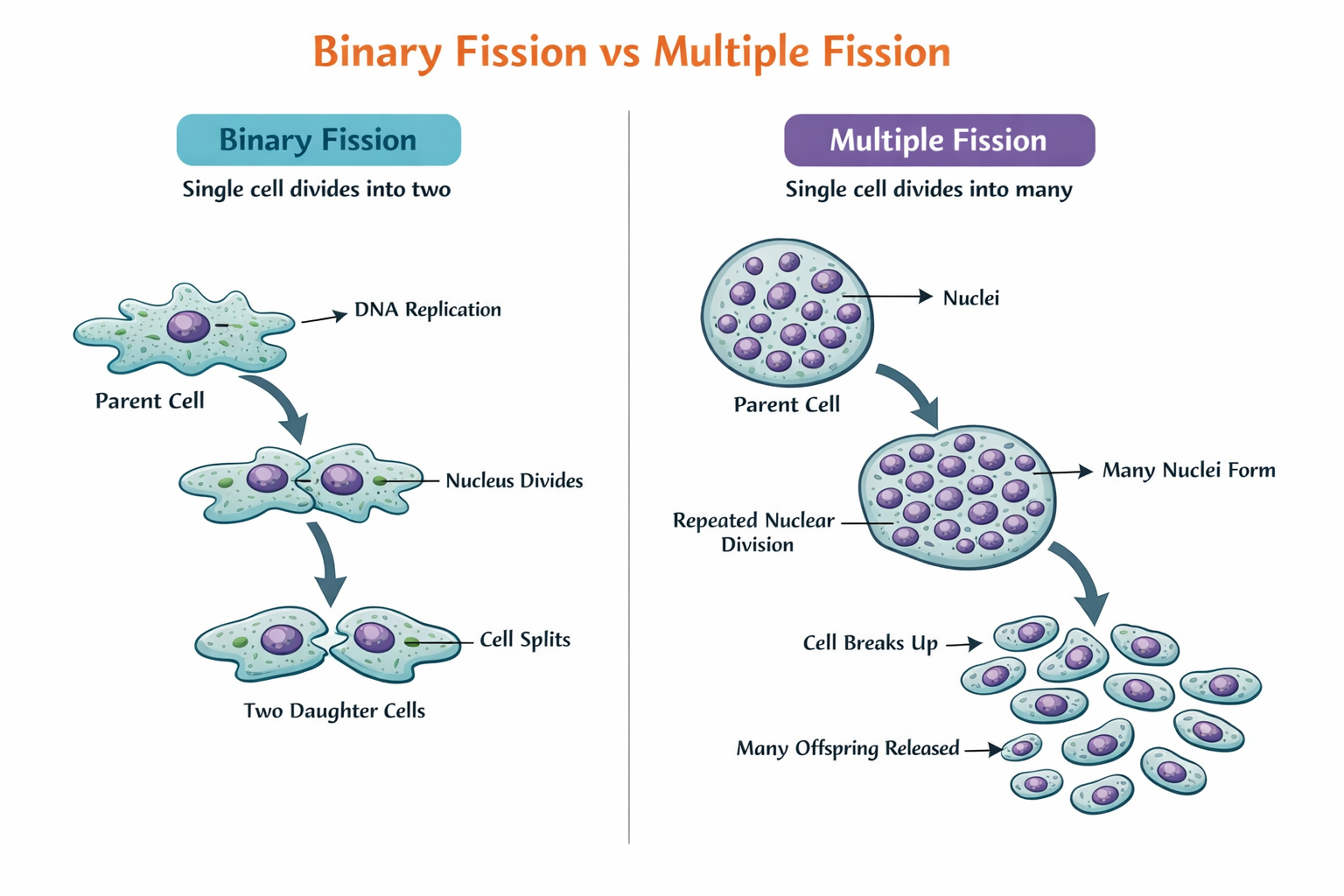
Chatgpt
In contrast, multiple fission involves the division of the nucleus multiple times before the cell divides. After repeated nuclear divisions, the cytoplasm divides simultaneously to form many daughter cells at once. This type of fission generally occurs under unfavourable conditions and is observed in organisms such as Plasmodium. When conditions become favourable again, the multiple daughter cells are released and grow into new organisms.
Q.6 What functions are performed by the testes in humans?
Answer:
The testes, or testis when referred to as singular, are the male primary reproductive organs in human males. Their main job is the production of sperm as well as secreting different hormones which are called sex hormones. There are two principal functions that can be recognized in the tests. The first one is the male gamete, or sperm, production and release which are the main parts of the fertilization process. The fertilization is in fact the zygote formation process which eventually culminates into an embryo and then a baby. The second function is the production of the male hormone testosterone which is the one responsible for the appearance of secondary sexual characteristics in boys like facial hair, deep voice, and muscular growth.
Q.7 What is the reason for menstruation?
Answer:
Menstruation is an ordinary and cyclical physiological process that takes place monthly in females of childbearing age, commencing with their adolescent years or puberty, and consists of the discharge of blood and mucus through the vagina. The typical menstrual cycle which is approximately 28 days long witnesses the liberation of a single ovum from the ovary. Additionally to the ovum, the endometrium, which is the lining of the uterus, grows thicker to the point that it can accept the implantation of a fertilized egg by supplying the essential nutrients. If however, no fertilization occurs, the endometrium is lost in shedding through the vagina thus indicating the beginning of menstruation. Menstruation is the process during the menstrual cycle when the uterus lining disintegrates and is removed.
Q.8 In what ways do the modes of reproduction differ in unicellular and multicellular organisms?
Answer:
Reproduction in unicellular organisms is done by complete cell division, as a single cell does all the life functions. The most common methods are binary fission and budding. On the other hand, multicellular organisms have specialised reproductive organs, making the process of reproduction more complicated. The latter group of organisms undergoes one of the following kinds of reproduction: vegetative propagation, spore formation, or sexual reproduction. Higher multicellular organisms like humans and flowering plants mainly resort to sexual reproduction as their prime mode.
Q.9 What are the main consequences of reproduction in terms of the stability of the species populations?
Answer:
The species population stability is ensured through the constant new individual production that is genetically similar to their parents, thereby continuously replacing them. The same reason is what eventually leads to the extinction of the species throughout the ages. Moreover, the process of reproduction introduces mutations in the offspring, which then allow the populations to adapt to the environmental changes more quickly. Therefore, reproduction with the same number of individuals in the population is not only a factor contributing to the eventual extinction of a species.
Q.10 Draw a labelled diagram of the longitudinal section of a flower.
Answer:
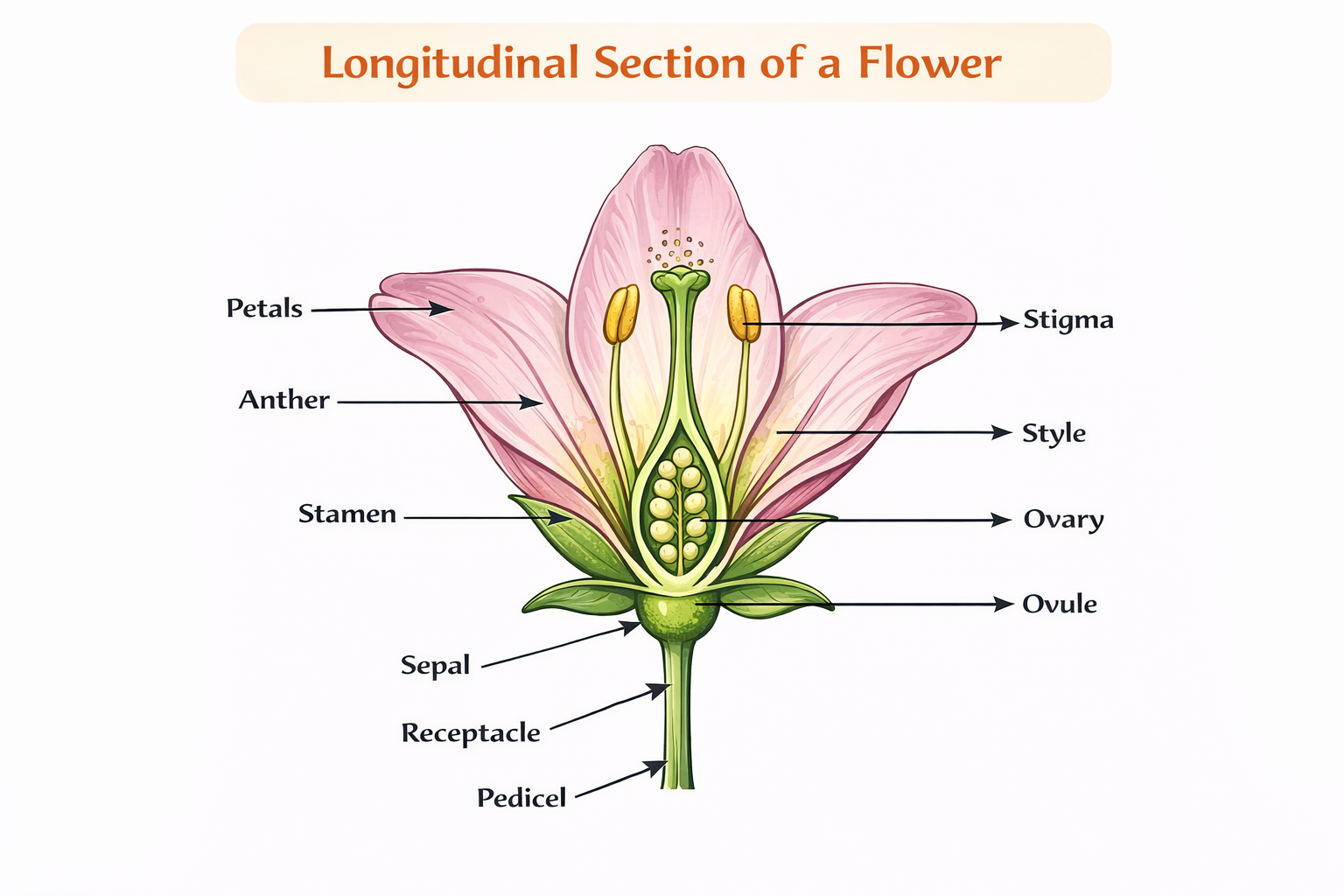
Chatgpt
Links For Chapter-wise NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
FAQs
1. Are menstruation and ovulation one and the same thing?
Menstrual and ovulation cycles are contrary to each other and they have different phases. The first one is the end of the second one – the process of ovulation in which the ovary releases a mature egg usually occurs during the middle of the cycle. Conversely, menstruation is the breakdown of the uterus lining which one can see as menstrual blood because there has been no fertilization.
2. Is it always the case that sexual reproduction is better than asexual reproduction?
It is not the case that sexual reproduction is always better than asexual reproduction. The choice of reproduction method depends on the environmental factors. Moreover, sexual reproduction produces genetic variability which facilitates the adaptability of the species to the changing of the surroundings. Asexual reproduction, on the contrary, permits quick multiplication and is very efficient in the case of stable conditions.
The assumption that sexual reproduction is always the winner is a myth. In ideal conditions, quick asexual reproduction methods like binary fission that organisms such as Amoeba undergoes are very efficacious. Yet, in case of change, sexually produced populations have better survival odds due to genetic variation. Thus, the best method is the one that survives and thrives in the specified environment conditions.
3. Is budding just another form of fission?
No, budding and fission are two distinct processes. In budding, a new individual arises from the parent’s body in the form of a small projection, e.g. in Hydra. The parent creature is not destroyed in this process. On the contrary, in fission, the whole parent organism splits into two or more daughter cells, for instance, in Amoeba.
4. Will fertilization be the ultimate necessity for spores to evolve into new organisms?
The answer is no, spores can develop without fertilization. Spores are the units of asexual reproduction which can grow into new organisms directly when the conditions are right. This type of reproduction is very common among fungi like Rhizopus. Spores are generally very tough and can endure extreme environmental conditions.
5. Is it the case that the PDFs of NCERT Solutions only comprise the final answers?
No, NCERT Solutions consist of more than just final answers. The tutorial for each solution is given in detail, which makes it easier for the learner to comprehend the thought-process behind that specific answer. This technique not only gives a stronghold on the concepts but also hones one’s skill in answer writing which is an integral part of efficient exam preparation.







