- Science Chapter 8 Class 10 - Quick Overview on Light Reflection And Refraction
- Download PDF of NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Light Reflection And Refraction
- Topics Covered In Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Light Reflection and Refraction
- Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 NCERT Solutions: Key Features
- Conclusion
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 – Light Reflection and Refraction
- Links for Other Chapter-wise NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
- FAQs
Science Chapter 8 Class 10 – Quick Overview on Light Reflection And Refraction
The Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Notes are essential for students to grasp not only the reflection of light but also the refraction when passing through different media. Among the main topics of the chapter are the formation of images by mirrors, the role of lenses in vision correction, and the reason why an object looks differently when observed through water or glass. All concepts are delivered step by step with uncomplicated illustrations and diagrams, hence making the understanding of even the difficult subjects very easy.
Many students have trouble memorizing the laws that govern the behaviors of light when it interacts with surfaces and solids. The same might not be the case if they had access to ToppersSky, which would be like having a personal tutor who breaks everything down and guides you through each step. Thus, being able to comprehend the common questions asked and being able to do the mathematical portions without any problem are some of the advantages one gets from these notes. And these notes are a must for students to do their last minute revision before the exams.
This particular chapter is of great importance in the Physics section and usually plays a big part in the board exams as questions concerning mirrors, lenses, and image formation often come up. To make the significance of this topic clear in the whole exam scheme, pupils are recommended to take a look at the CBSE Class 10 Science syllabus. For even more efficient revision, consider moving to a different chapter through Class 10 Science Revision Notes.
Download PDF of NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Light Reflection And Refraction
Topics Covered In Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Light Reflection and Refraction
| List of Topics Covered in Science Chapter 9 Class 10 | |
|---|---|
| Topics | Subtopics |
| Reflection of Light | |
| Spherical Mirrors | Image formation by spherical mirrors, Representation using ray diagrams, Sign convention, Mirror formulas and magnification |
| Refraction of Light | Reflection through a rectangular glass slab, the refractive index, Refraction by spherical lenses, Image formation using ray diagrams, Sign convention, Lens formula and magnification, Power of a lens |
Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 NCERT Solutions: Key Features
The question and answer solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 offered in the NCERT book are very helpful for students to have good board examination results. Besides, a clear notion of phenomenon is a must, and that is done so through NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 indeed. Below are some important points about these solutions:
- PDF file of Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Questions and Answers is made by the experts in the subject whose academic experience is very strong and thus it is a reliable source for exam preparation.
- All the answers have been explained with the help of clear charts and well labeled diagrams that make understanding the difficult concepts easy.
- The use of the mirror formula for deriving and applying for concave and convex mirrors is explained gradually.
- The primary target of the solutions is to help students secure the highest marks in the examinations.
- The phenomenon of light passing through a glass slab and the idea of lateral displacement are explained meticulously along with diagrams.
- The basic physics behind the working of optical devices such as microscopes and telescopes is discussed openly in order to reinforce the understanding of the concepts.
- The solutions are also available in PDF format free of cost which means that students can easily download them and study offline. The layout is also user friendly which means that navigation is smooth.
Conclusion
The Class 10 Science Chapter 9 question–answer solutions offer easy, plain, and comprehensive clarifications of all major ideas concerning light reflection and refraction. It is highly recommended for students to download and consult these expert-prepared NCERT solutions as they will not only provide a rapid overview of the chapter but also teach them the art of forming correct answers in examinations. To support students in gaining the required knowledge and skills, a routine revision of these solutions will be their confidence builder and allotment of better grades in the end.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 – Light Reflection and Refraction
Q.1 What is the principal focus of a concave mirror?
Answer:
When light rays parallel to the principal axis fall on a concave mirror, they converge at a point on the principal axis after reflection. This point of convergence is called the principal focus of a concave mirror.
Q.2 Which mirror gives an erect and enlarged image of an object?
Answer:
A concave mirror forms an erect and enlarged image when the object is placed between the pole and the principal focus of the mirror. The image formed in this case is virtual and upright. Convex and plane mirrors do not produce enlarged erect images.
Q. 3 Why is a convex mirror preferred as a rear-view mirror in vehicles?
Answer:
A convex mirror always forms an erect and diminished image of objects placed in front of it. It provides a wider field of view, allowing the driver to see a larger area behind the vehicle. Therefore, convex mirrors are preferred as rear-view mirrors.
Q. 4 When a light ray travelling in air enters obliquely into water, does it bend towards or away from the normal? Give a reason.
Answer:
When light travels from a rarer medium (air) to a denser medium (water), it bends towards the normal. This happens because the speed of light decreases while entering the denser medium.
Q.5 Which of the following materials cannot be used to make a lens?
(a) Water
(b) Glass
(c) Plastic
(d) Clay
Answer:
(d) Clay
Clay cannot be used to make a lens because it is opaque and does not allow light to pass through.
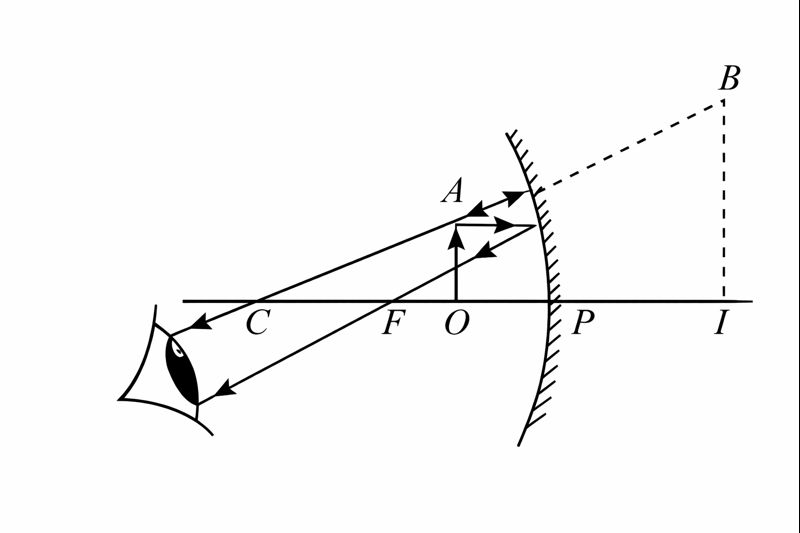
Q.6 The image formed by a concave mirror is virtual, erect, and larger than the object. Where should the object be placed?
(a) Between the principal focus and the centre of curvature
(b) At the centre of curvature
(c) Beyond the centre of curvature
(d) Between the pole and the principal focus
Answer:
(d) Between the pole and the principal focus
When the object is placed between the pole and the principal focus of a concave mirror, the image formed is virtual, erect, and magnified.
Chatgpt
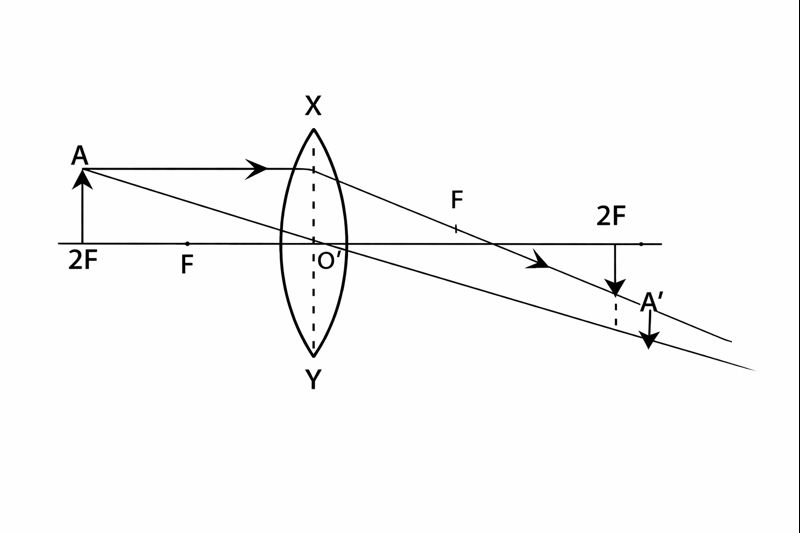
Q.7 Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens to obtain a real image of the same size as the object?
(a) At the principal focus of the lens
(b) At twice the focal length
(c) At infinity
(d) Between the optical centre and the principal focus
Answer:
(b) At twice the focal length
Chatgpt
Q. 8 A spherical mirror and a thin spherical lens each have a focal length of
−15cm. The mirror and the lens are likely to be:
(a) Both concave
(b) Both convex
(c) The mirror is concave and the lens is convex
(d) The mirror is convex and the lens is concave
Answer:
(a) Both concave
Explanation:
A negative focal length indicates a concave mirror and a concave lens, as their principal focus lies on the same side as the object. Therefore, both the mirror and the lens are concave.
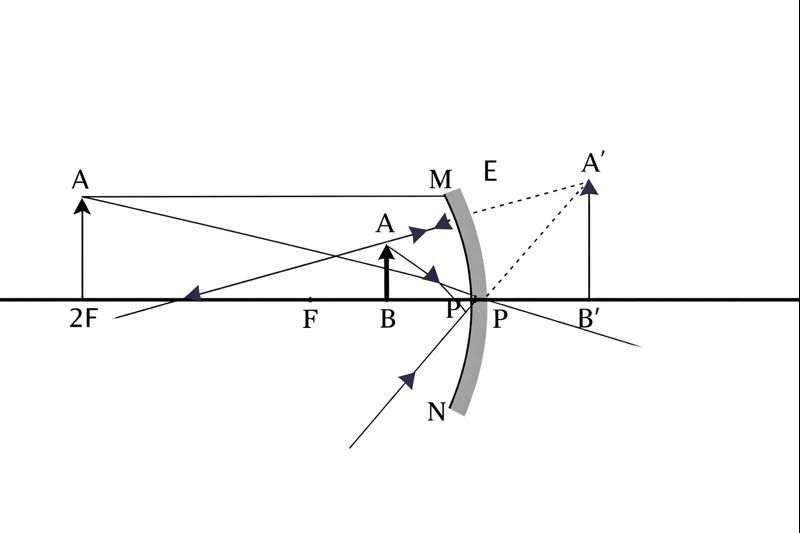
Q.9 We wish to obtain an erect image of an object using a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm.
What should be the range of distance of the object from the mirror?
What is the nature of the image?
Is the image larger or smaller than the object?
Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
Answer:
To obtain an erect image using a concave mirror, the object must be placed between the pole (P) and the principal focus (F) of the mirror.
Given:
Focal length of the concave mirror, 𝑓=15cm
Range of distance of the object:
The object should be placed at a distance less than the focal length, i.e.,
0cm < Object distance < 15cm
Nature of the image:
- The image formed is virtual
- The image is erect
- The image is formed behind the mirror
- Size of the image:
- The image is larger (magnified) than the object
When an object is placed between the pole and the principal focus of a concave mirror, a virtual, erect, and magnified image is formed.
Chatgpt
Q.10 One-half of a convex lens is covered with a black paper. Will this lens produce a complete image of the object? Verify your answer experimentally and explain your observations.
Answer:
Yes, the lens produces a complete image of the object with less intensity. Consider the following two cases:
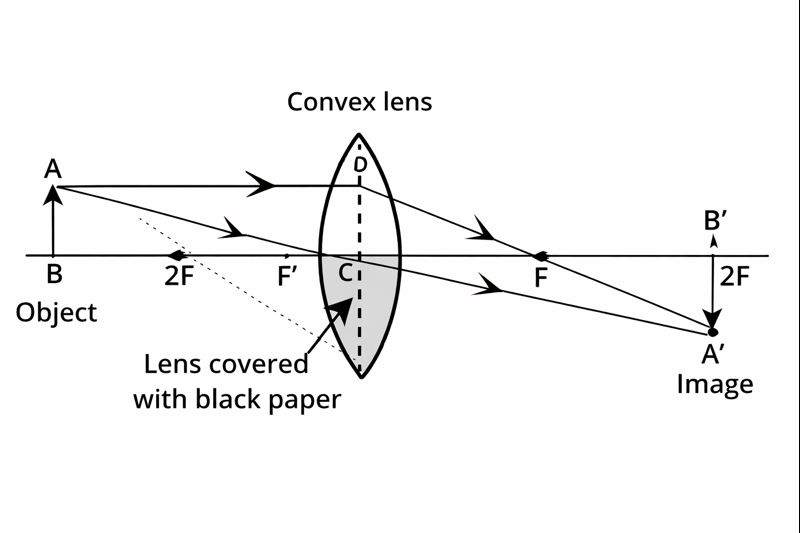
Initially, the lower section of the lens is obscured with dark paper. The light rays emitted from the object get refracted only through the upper section and the image is created, while in the lower section the light rays are obstructed.
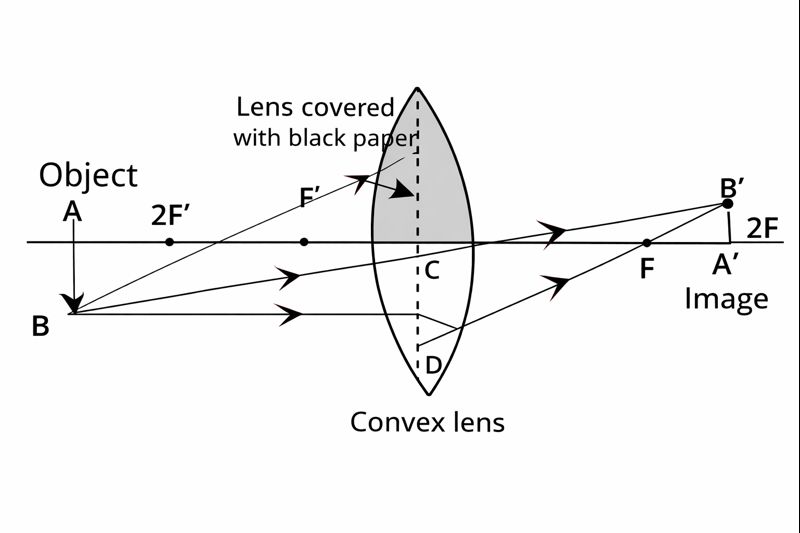
In the second situation, the upper side of the lens is blocked with dark paper. The light rays emitted by the object go through the lower part of the lens, are refracted and the image is formed meanwhile the upper part is completely dark due to the obstruction of the light rays.
Thus, a decrease in the intensity of the image is noticed, that is, the intensity of the image is lower, and the entire image is formed.
Links for Other Chapter-wise NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
FAQs
1. What is the difference between reflection and refraction of light?
Reflection of light occurs when light rays strike a surface and bounce back into the same medium. In this process, the direction of light changes, but it continues to travel in the same medium.
Refraction of light occurs when light passes from one medium to another (such as air to water). During refraction, light changes its direction as well as its speed due to the change in the optical density of the medium.
2. What are the laws of reflection of light?
The laws of reflection state that the incident ray, reflected ray, and normal all lie in the same plane, and the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. These laws apply to all reflecting surfaces including plane mirrors, concave mirrors, and convex mirrors.
3. What is the mirror formula and how is it applied?
The mirror formula is 1/f = 1/v + 1/u, where f is focal length, v is image distance, and u is object distance.
4. What is total internal reflection and when does it occur?
Total internal reflection occurs when light traveling from a denser medium to a rarer medium strikes the interface at an angle greater than the critical angle. In this phenomenon, light is completely reflected back into the denser medium without any refraction occurring.
5. How does refraction cause apparent depth and other optical illusions?
Refraction makes objects appear at different positions than their actual locations due to light bending at interfaces. Water appears shallower than its actual depth, and objects in water seem closer to the surface because light rays bend away from normal when traveling from water to air.







